Navigating through a Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy can feel akin to steering an oil tanker through a hurricane. 90% of businesses end up floundering, their strategic objectives lost in the storm. Think of this article as your lifeline, your reliable compass that will guide you through the tempestuous seas of strategy implementation, ensuring you’re among the triumphant 10%.
There’s a key reason why only a handful reach their desired harbor unscathed – they know how to effectively apply their go-to-market strategy. As elusive as a mermaid’s song, it’s this practical application that turns a strategy from mere paper plans into solid business gains.
In the swirling churn of business strategy, the ability to harness practical implementation can be your anchor, keeping you grounded amidst the chaos. Time to hoist the sails, chart your course, and stand out among the rest.
Understanding GTM Strategy Development: The Key to Your Business Success
- Unravel the essence of go-to-market strategy development.
- Perceive the significance it provides to your business.
- Get acquainted with the vital elements a successful GTM strategy should entail.
What is GTM Strategy Development?
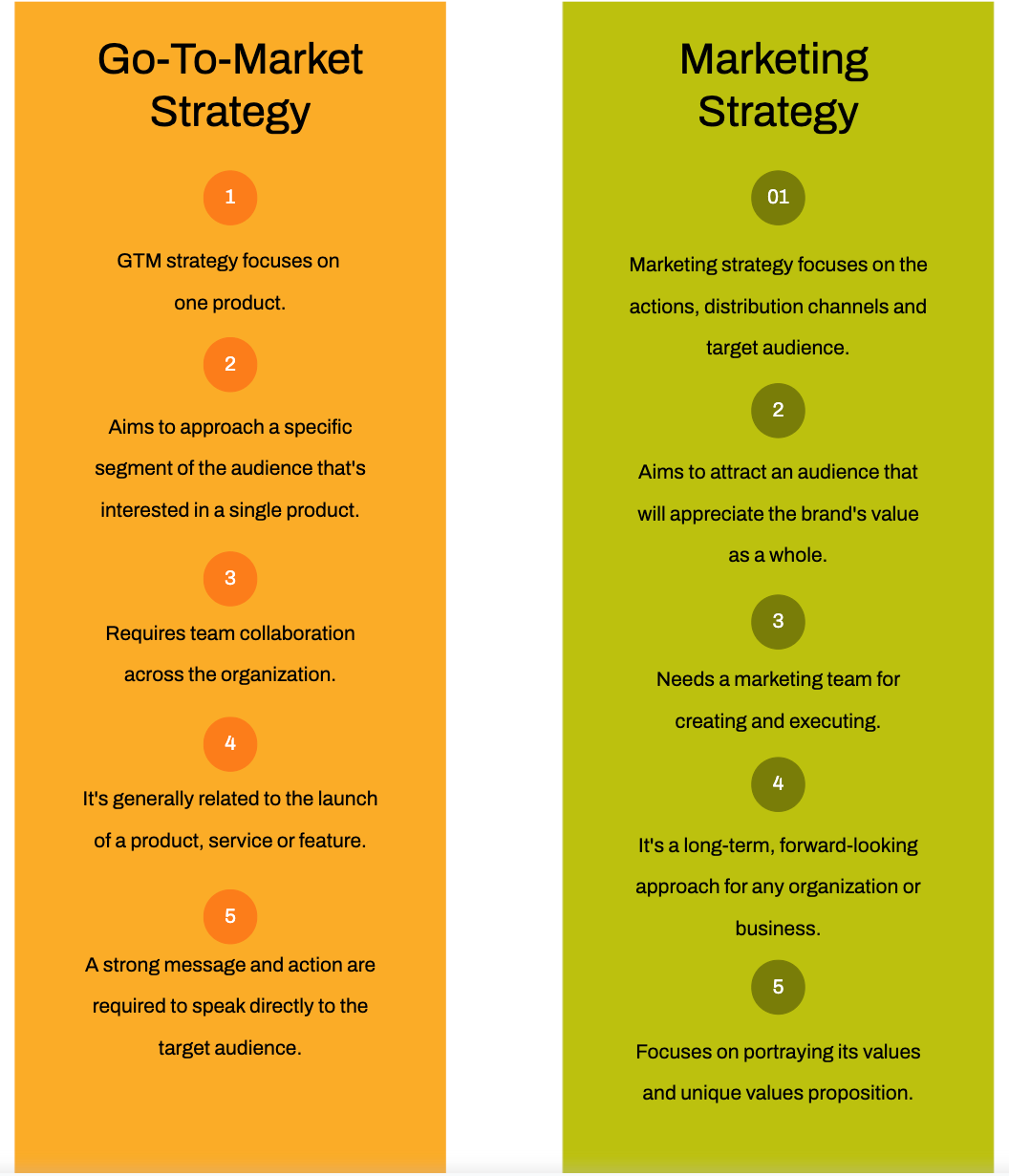
Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy is the plan that aligns all the business functions to successfully deliver a product or service to the end customer and achieve competitive advantage. Go-to-market strategy development, therefore, is the process of creating this detailed action plan.
Often overlooked in favor of other operational tasks, GTM strategy development serves as the blueprint for your business actions, laying a solid foundation for the effective execution of your vision.
A well-crafted GTM strategy can light the path, ensuring every decision aligns with your business goals and targets the right audience.

Why is GTM Strategy Development crucial for your business?
In a saturated business landscape where 90% of businesses have difficulties executing their GTM strategies effectively, a comprehensive go-to-market strategy proves to be not just an asset but a necessity.
Your GTM strategy acts as a roadmap, guiding your business through the market landscape, avoiding common pitfalls, and steering clear from the directionless wandering that often leads to failure.
Crucially, it helps:
- Identify your target audience
- Understand competitive dynamics
- Define your unique value proposition
- Lay out the specific steps you need to take to deliver your product or service effectively
Key components of a successful GTM Strategy Development
An effective GTM strategy Framework relies on several key components:
- Define the Target Market: Understanding who you’re trying to reach is the first fundamental step in crafting an effective go-to-market strategy. Analyzing the customer persona and their demographics and psychographics helps tailor your product and marketing efforts to resonate with their specific needs and preferences.
- Craft the Value Proposition: Your value proposition demonstrates why customers should choose your product or service over your competitors. Understanding your unique offerings and how they solve the customer’s problem or improve their situation is crucial.
- Determine the Sales and Marketing Channels: Any GTM strategy should detail which channels to use to reach and persuade your target market, be it through direct sales, online marketing, resellers, or partners. Appropriate selection of these channels is quintessential for an effective sales strategy and customer acquisition, engagement, and retention.
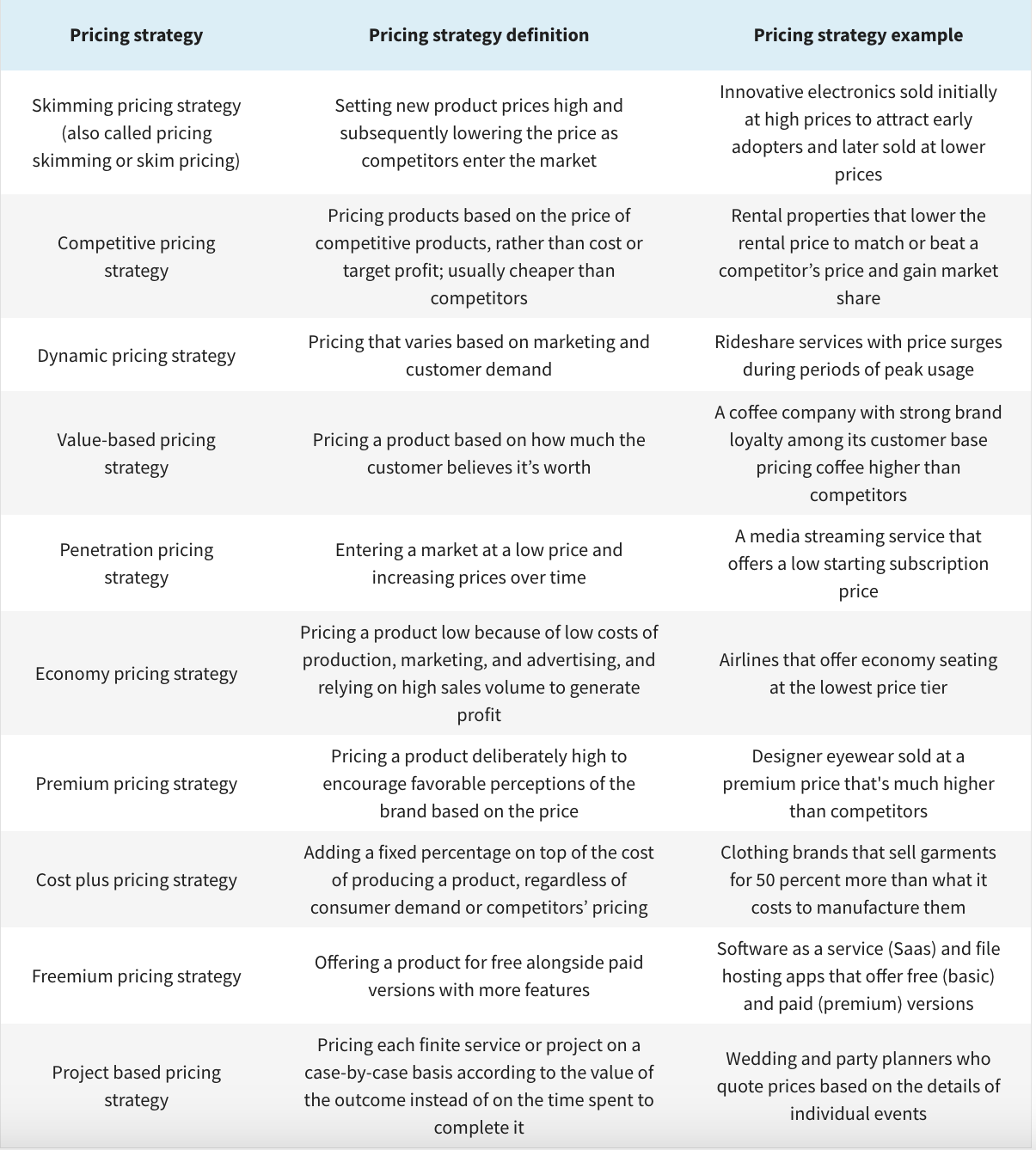
- Structure Your Pricing: Pricing shouldn’t be a numerical afterthought. It’s a strategic element that can significantly influence the perceived value of your offering. Pricing strategy should consider both market conditions and the customer’s willingness to pay.
GTM strategy development is essential to your business success and provides a clear path towards achieving your business goals. By considering each of these elements, you can tailor a strategy that resonates with your target audience and succeeds in the marketplace.
Mastering GTM Strategy Execution: Avoiding Common Pitfalls
- Outlining an effective go-to-market strategy execution guide
- Highlighting how to anticipate and sidestep common pitfalls in go-to-market strategy execution
- Providing real-life examples for successful GTM strategy execution for better understanding
Benefits: Get an actionable guide to execute your go-to-market strategy seamlessly, learn to dodge common missteps, and gain inspiration from successful real-life case studies.
Step-by-step guide to executing your GTM Strategy
Solid strategy execution is as crucial as having a robust plan. Here’s a breakdown of the three main steps on how you can methodically implement your GTM strategy:
- Defining Goals and Metrics: Start by defining concrete goals and metrics. Your goals might include expanding into a new market, increasing market share, or others. Your metrics should be quantifiable and clear. Are you targeting a 30% increase in sales? A user base of 100,000 in a new market?
- Aligning Teams: Align your marketing, sales, and product teams. Everybody should be on the same page about the plan, the target audience, and the desired outcome. Encourage frequent communication among teams to ensure better coordination.
- Identifying Key Channels: Identify the best channels to reach your target audience. This could be social media, email marketing, content marketing, SEO, or others. Testing multiple channels and zeroing in on what works can be part of the strategy.

Common mistakes in GTM Strategy Execution and how to avoid them
As with any business strategy, the road to GTM success is littered with potential pitfalls. Knowledge of these common mistakes can help you avoid them. The two most common include:
- Not Updating the GTM Strategy: A go-to-market strategy isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it plan. The business landscape and consumer behaviour are always changing. Consider updating your strategy regularly, based on analytics data and market trends.
- Neglecting Customer Feedback: Customer feedback is a goldmine of actionable insights. Ignoring it is a costly mistake. Use feedback to identify pain points and enhance your product or service accordingly.
Real-life examples of successful GTM Strategy Execution
Learning from successful real-life examples can be invaluable. They can offer insights into practical strategies and inspire creative solutions.
When Slack entered the market, it already had strong competitors. But the company stood out by focusing on user experience. They made their product fun, easy to use, and turned it into an indispensable work tool, inspiring a new wave of productivity apps.
Airbnb’s go-to-market strategy is another excellent example. They focused on creating a strong community of hosts, providing them with the resources they needed to succeed. This created a loyal user base and helped Airbnb dominate the market.
By understanding how these successful businesses have leveraged their GTM strategies to thrive, you can refine and execute your own strategy effectively, avoiding common pitfalls along the way.

GTM Strategy Mistakes: Learn from Others’ Failures
- Businesses often stumble when implementing GTM (Go-to-Market) strategies, but we can sidestep those pitfalls.
- Real-life examples provide tangible lessons for refining our approach.
- Knowing what to avoid is often just as important as understanding what to do.
Top mistakes businesses make in GTM Strategy Implementation
Implementing a go-to-market strategy often seems straightforward on paper. Yet, many businesses stumble on the same hurdles, often falling short of their goals. These primarily involve failures in market assessment, communication, product alignment, and flexibility.
- Failure to accurately assess your market: You might have an innovative product, but if it’s not meeting a market need, or if the competition is too stiff, you will struggle. For GTM plans to succeed, robust market assessment isn’t an option- it’s a necessity.
- Communication missteps: Miscommunication within teams, with stakeholders, or with the market can wreak havoc on the best-laid plans. Clear, consistent communication is critical at every step of implementation.
- Lack of product-alignment: If your GTM strategy doesn’t align with your product’s features, benefits, and unique selling points, your strategy may misfire. Understanding and leveraging your product’s strengths in your GTM plan is non-negotiable.
- Lack of flexibility: In today’s fast-paced, highly volatile market, adaptability is the name of the game. If your strategy is too rigid and doesn’t allow for pivots based on market feedback, business intelligence, or unexpected challenges, it will likely falter.
Case studies of failed GTM Strategy Implementation
Unfortunately, the business landscape is littered with examples of GTM strategies that missed the mark. While it’s not exactly schadenfreude we’re after, these cases offer valuable learnings.
Take the case of Quibi, for example. The company underestimated its market, led by an ineffective communication strategy, resulting in a go-to-market strategy that quickly floundered in the midst of the 2020 pandemic.
Or consider HP’s TouchPad, which failed to gain market traction because of a lack of differentiation and a GTM strategy that overestimated their product’s appeal and capabilities.
Each of these cases underscores the importance of understanding and avoiding the aforementioned mistakes when crafting and implementing a GTM strategy.
Lessons learned from these mistakes and how to avoid them in your business
If there’s a silver lining to these failure case studies, it’s that they offer tangible lessons that can guide your GTM planning and execution.
- The lesson from failed market assessment? Market research isn’t a luxury-it’s the bedrock of a robust go-to-market strategy. Thoroughly understand your target audience, competitors, and industry trends before crafting your strategy.
- To sidestep communication missteps, institute strong internal and external communication protocols. Keep your team aligned, your stakeholders informed, and your messaging to the market clear and consistent.
- To avoid product-alignment pitfalls, ensure a deep understanding and prominent inclusion of your product’s USP in your GTM strategy. Leverage your product’s strengths and highlight its differentiation points.
- To avoid the pitfall of inflexibility, build an agile strategy. Expect bumps in the road and be open to refine and reorient your strategy based on real-time feedback and evolving market dynamics.
While implementing a GTM strategy is undoubtedly challenging, awareness of potent pitfalls can empower you to sidestep them and position your business for full-throttle success.
GTM Strategy Success Factors: What Sets Successful Businesses Apart
- Discover the pivotal factors for a successful GTM strategy.
- Learn the practical application of these key success factors into your GTM strategy.
- Benefit from insights drawn from businesses that have nailed their GTM strategy.
Key Success Factors in GTM Strategy Implementation
The realm of successful go-to-market strategy lies within a few critical success factors. Embarking on a successful GTM strategy isn’t about blindly deploying numerous tactics. It’s more about a targeted approach focused around crucial factors.
Firstly, a well-defined target market forms the backbone of any successful GTM strategy. Knowing your target audience allows for more precise decision-making and resource allocation. Deeply understanding who your potential customers are and their pain points fosters a resonance that’s essential in today’s crowded markets.
Secondly, a clear value proposition that communicates the unique benefits your product or service provides is essential. This doesn’t mean simply informing customers of your product’s features but making clear the specific problems you’re solving for them and why you’re better than alternatives.
![[Old Product UI] Product marketing launch project in Asana, spreadsheet-style view with project deliverables (Lists)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/f8492eda-b918-4cf6-868a-556899ee6d63/inline-what-are-project-deliverables-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
How to incorporate these success factors into your GTM Strategy
Implementing these success factors into your go-to-market Strategy can be a game-changer. Start by undergoing a comprehensive target market analysis. Use this to create a data-driven customer profile which then informs all elements of your GTM strategy from brand messaging to sales channels.
To craft a compelling value proposition, begin by understanding not just the features of your product or service, but how these translate into benefits for your customers. Combine this understanding with knowledge of your competition, carving out a unique niche for your offering.
Case studies of businesses that successfully implemented their GTM Strategy
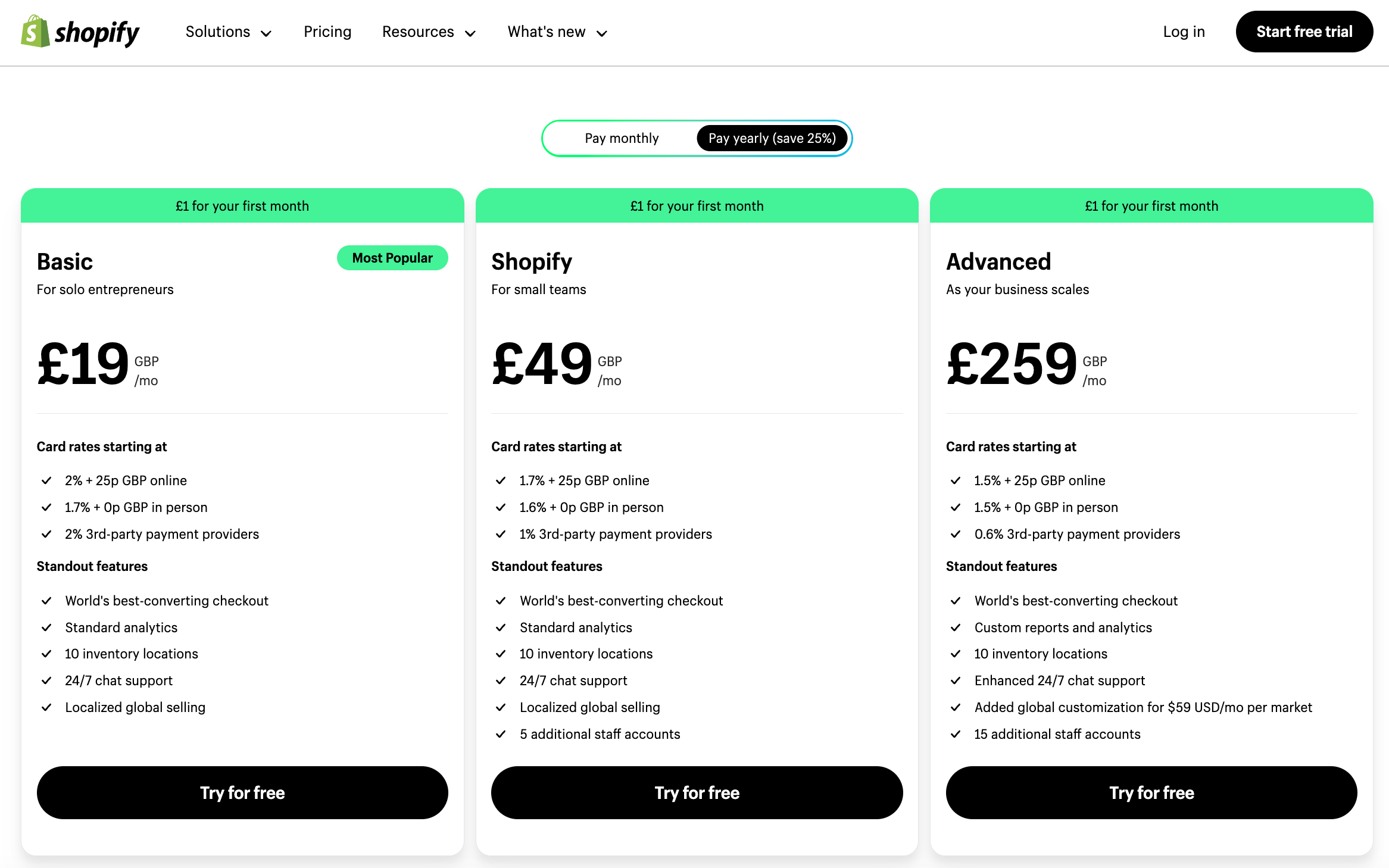
Real-world case studies can illustrate the application of these success factors effectively. For instance, Shopify understood early on that their target audience consisted of small to medium businesses looking to sell online.
They positioned themselves as a simple-to-use e-commerce platform allowing anyone to start an online store. Their go-to-market strategy focused on providing these businesses with an easily accessible, cost-effective solution, demonstrating the effectiveness of a well-executed GTM Strategy.
The strategic application of these success factors is instrumental in driving an effective GTM Strategy. Armed with this knowledge, businesses can avoid common pitfalls, effectively maneuvering themselves closer to establishing a strong market presence.
GTM Strategy Best Practices: Ensuring Your Business Success
TL;DR
- Identifying and applying best practices for successful GTM strategies.
- Making these best practices integral components of your go-to-market strategy.
- Impact on business success through the incorporation of these best practices.
Best practices in GTM Strategy Development and Implementation
Strategy matters. No two businesses are the same, and what works for one may not work for the other. A tailored go-to-market (GTM) strategy that reflects your business model, target market and unique selling proposition is essential.
- Market research: Understanding your target market, their needs, and, most importantly, their pain points. A key best practice is to develop an Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) that guides your GTM strategy.
- Determine your unique selling proposition: How is your product/service different or better than what is currently offered? This value proposition will form the heart of your go-to-market plan.
- Channel selection: Choose the right channels to deliver your product/service to your target customers. This could be a blend of digital and physical channels, depending on your market research findings.
How to incorporate these best practices into your GTM Strategy
A successful go-to-market strategy is not a one-time event. It’s a cycle. A continuous cycle of:
- Planning
- Implementing
- Reviewing
- Refining
Start with your ICP and value proposition. Use them as a foundation to build your business’s go-to-market strategy.
The strategy should include selection of appropriate channels based on your market research, your unique positioning, and a meticulously planned launch. Factor in post-launch activities such as monitoring, evaluation, and iterative improvements.
Feedback is crucial. Regularly garner feedback from target customers and be open to making changes in your marketing strategy based on this feedback.
.png?width=672&name=ideal-customer-profile-infographic1%20(1).png)
The impact of these best practices on your business success
The best practices are not just abstract ideas. They have tangible impacts on your business’s success. By following these best practices, your GTM Strategy could lead to:
- A successful product launch
- An increase in market share
- Overall business growth
A well-executed GTM strategy can also position your business as a trusted and reliable provider in your market. This can enhance brand reputation and foster customer loyalty, which ultimately contributes to long-term business success.
The GTM strategy is not just about making sales or gaining market share, it’s about building a sustainable business. The right strategy will help you navigate the complex business environment and ensure your sales and marketing teams thrive in the long term.
Steering Clear of GTM Pitfalls – Your Key to Success
Remember, successful GTM implementation depends heavily on well-defined goals, robust planning, impeccable execution, and earnest learning from mistakes. With barriers such as lack of resources, unrealistic expectations, or misaligned strategies out of the way, the victory is within your grasp.
Not just applicable knowledge, the understanding shared in this article bears significant financial potential. Failing GTM can prove costly – dodging this pitfall is the exact money-saver your business requires.
Now, equipped with this intel and insight into common stumbling blocks, it’s your turn to implement a bullet-proof GTM strategy. Consider an internal audit of your GTM plan, identify potential areas of improvement, and act upon them swiftly.
Does your current GTM strategy consider the potential obstacles highlighted here? Reflect on how you can turn this newfound understanding into actionable steps for your company.
The road to business success isn’t always easy, but avoiding the GTM pitfalls that have claimed 90% of your competitors will give you a commanding edge in the race. Don’t let history repeat itself –gearing up for success starts with altering your GTM narrative.
Glossary of Terms
- Go-To-Market (GTM) Strategy: A plan that outlines how a company will reach customers and achieve a competitive advantage when launching a new product or service.
- Value Proposition: A statement that explains why a customer should choose a particular product or service, highlighting its unique benefits and differentiators.
- Target Market: The specific group of consumers at which a product or service is aimed.
- Customer Persona: Semi-fictional characters that represent the ideal customer, based on market research and real data about existing customers.
- Sales Channels: Means through which a company delivers its products or services to customers (e.g., direct sales, online, retail).
- Marketing Channels: Platforms used to communicate with the target audience (e.g., social media, email, content marketing).
- Ideal Customer Profile (ICP): A detailed description of a fictitious entity that embodies the key characteristics of a company’s target customer.
- Market Assessment: The evaluation of market trends, competition, and customer needs.
- Product Alignment: The process of ensuring that a product or service aligns with market needs and the company’s GTM strategy.
- Feedback Loop: A system of gathering and using customer feedback to improve a product or service.
GTM Strategy Implementation FAQ
- What is the importance of a GTM strategy?
- A GTM strategy is crucial for aligning business functions and ensuring a successful product or service launch, helping a company reach its target market effectively.
- How do I define my target market?
- Defining your target market involves researching your potential customers’ demographics, needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- What makes a value proposition effective?
- An effective value proposition clearly communicates the unique benefits of your product or service and how it solves your customers’ problems or improves their situation.
- How often should a GTM strategy be updated?
- A GTM strategy should be reviewed and updated regularly to respond to changes in market conditions, customer needs, and business objectives.
- Can small businesses benefit from a GTM strategy?
- Absolutely. A GTM strategy is essential for businesses of all sizes to effectively enter a market and reach their target audience.
List of Resources
- Books
- “Crossing the Chasm” by Geoffrey A. Moore: Offers insights into marketing high-tech products in mainstream markets.
- “Blue Ocean Strategy” by W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne: Discusses creating uncontested market space and making the competition irrelevant.
- Websites
- Harvard Business Review (hbr.org): Provides articles and case studies on marketing strategies and business insights.
- Forbes – Marketing and Sales (forbes.com/marketing-sales): Offers latest trends and advice on marketing and sales strategies.
- Online Courses
- “Introduction to Marketing” by University of Pennsylvania (offered on Coursera): A foundational course in marketing principles.
- “Strategic Marketing for Entrepreneurs” by Cornell University (offered on eCornell): Focuses on developing marketing strategies for startups and entrepreneurs.
- Webinars and Podcasts
- “Marketing Over Coffee”: A podcast discussing both classic and new marketing tactics.
- “The GTM Show” by Leadfeeder: A podcast focusing on Go-To-Market strategies.
- Professional Associations
- American Marketing Association (ama.org): Offers resources, networking, and professional development in marketing.
- Sales and Marketing Executives International (smei.org): Provides certification, education, and networking opportunities for sales and marketing professionals.
Using these resources will help you deepen your understanding of GTM strategies and stay updated on the latest trends and best practices in the field.
Stay safe out there!

