This analogy mirrors the journey of piecing together a winning Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy for startups. You’re about to learn how vital this foundation is. Equipped with effective strategies and relevant case studies, we’ll dissect the construct of an efficient GTM strategy.
From identifying your ideal target market to crafting compelling value propositions and channel optimization. You’ll discover the frameworks behind successful startups, ultimately gaining the insights to shape the robust backbone of your venture.
Don’t merely build; construct with a winning GTM blueprint backing you.
Understanding GTM Strategy Framework for Startups
TL;DR
- Clarity on what a GTM Strategy is, and its crucial role for Startups
- A brief scan of how a GTM Strategy framework looks like and its implementation patterns.
What is GTM Strategy?
Go-to-market or GTM Strategy is a fluid action plan directing the path of a product or service to its consumer base. It outlines how a company will pitch, sell, and fulfill its product or service to its customers, a blueprint to achieve a competitive marketplace advantage.
With a strong go-to-market strategy, a startup gets a comprehensive roadmap, ensuring that they don’t lose sight of their goals in the heat of operations and can effectively solve customers’ problems.
The Lifeline for Startups
Counterintuitive as it may appear, startups are especially sensitive to their GTM strategy. With finite resources and an initial phase packed with uncertainties and instability, startups can’t afford to function with an inefficient GTM strategy.
A thoroughly researched and built GTM strategy helps startups:
- Navigate the tumultuous introductory phase
- Identify their intended customers
- Position their product in the market successfully
By aiming necessary shots in the right direction, startups can avoid unnecessary wastage of resources and save themselves from taking a debilitating hit.

An Introduction to GTM Strategy Framework
Next comes the GTM Strategy Framework. This is a structured plan breaking down the GTM strategy into various stages, capturing a range of aspects like:
- Identifying target customers
- Channel selection
- Pricing strategy
- Positioning strategy
It’s like the skeletal structure that holds together a GTM strategy - providing visibility, clarity, and a sense of direction for sales and marketing teams.
Building a Solid GTM Framework
Creating a rock-solid go-to-market strategy framework isn’t an overnight occurrence but a result of:
- Due diligence
- Market research
- Customer understanding
- Insightful input
Startups need to evaluate their customer demands, competitive landscape, pricing strategies, and sales channels. Doing so ensures that no stone is left unturned in their pursuit of crafting a winning GTM strategy.
This cycle allows them to consistently test, learn, and adapt their strategies, keeping them tuned in to the changing market dynamics, and ensuring that they rise to potential challenges, seizing opportunities as they come. Growing startups can build resilience to market flux, adapt quickly, and develop a proactive rather than a reactive strategic approach.
With an understanding of the GTM strategy and its framework established, the stage is now set to delve deeper.

Key Components of a Successful GTM Strategy
- This section reviews the critical parts of launching a successful GTM strategy.
- The focus will be on the identification of a target market, understanding the customer persona, and perfecting product messaging and positioning.
- Sales and marketing strategies, as well as pricing and revenue models for a winning GTM plan, are also discussed.
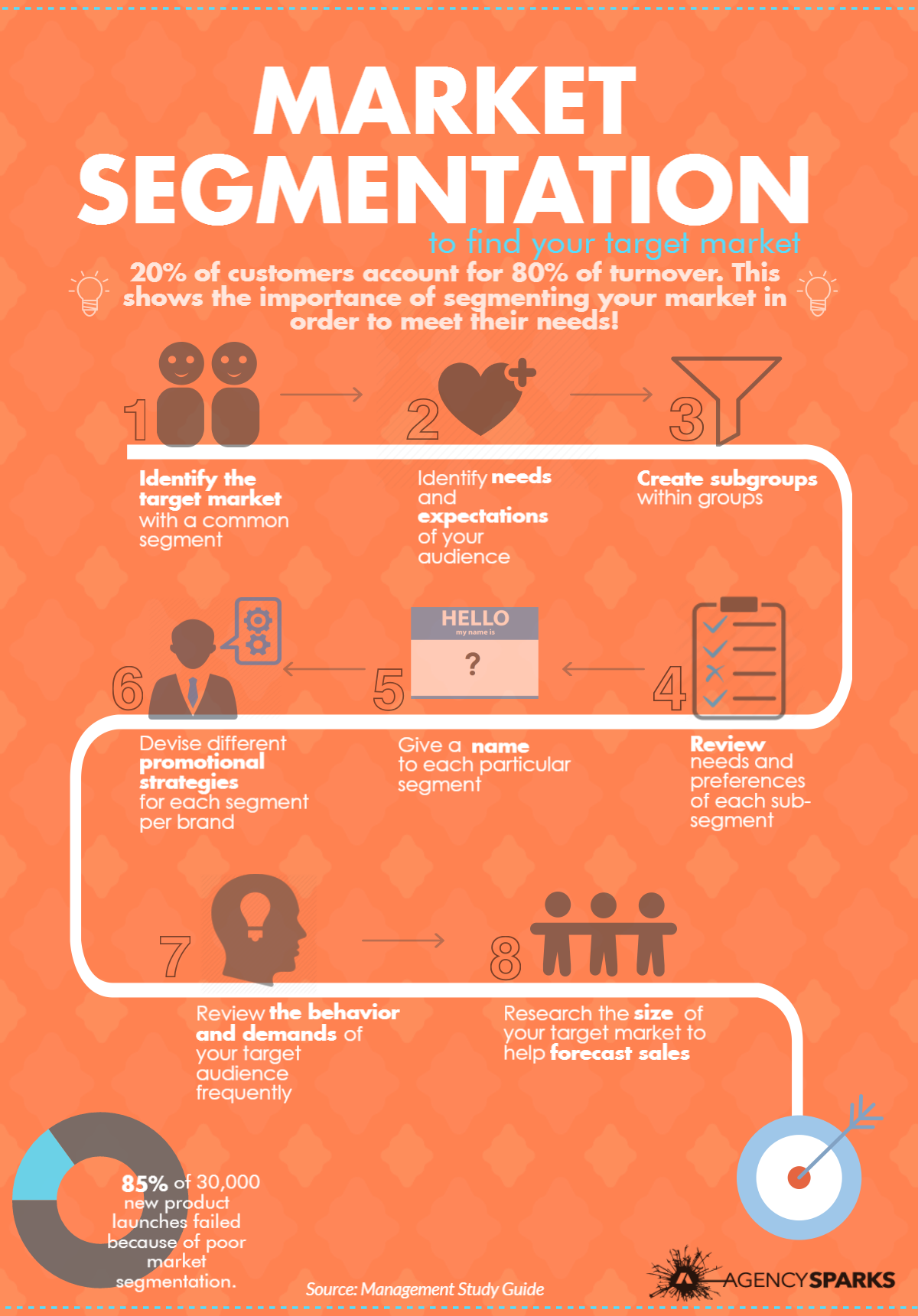
Identifying Target Market
A target market is the group of potential customers that a business is marketing its products or services to. The specifics this existing market is defined by are demographics, behavior patterns, preferences and more.
This audience is the segment of the market that is most likely to purchase your product or service. Selecting a target market affects all areas of operations from marketing and sales to product development and customer support.
Market segmentation goes hand-in-hand with Target market selection, dividing a broad market into submarkets, or segments. This can be segmented through geographic, demographic, psychographic, or behavioral means.
Understanding Customer Persona
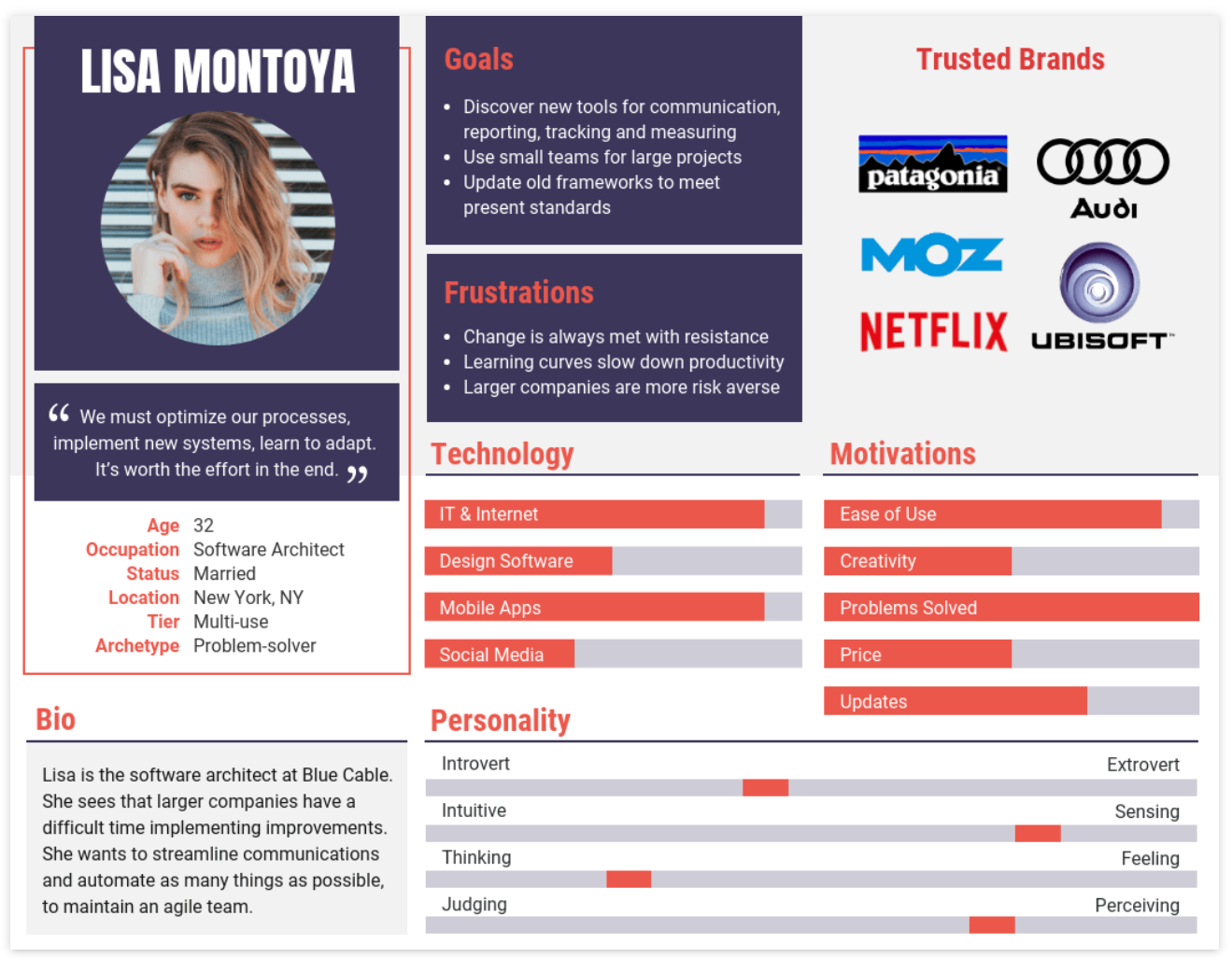
Customer personas embody your ideal customer. They typically possess:
- Specific characteristics
- Interests
- Issues
- Behavioural inclinations
Understanding customer personas is crucial. It allows you to form an idea of the practical considerations and emotional triggers that would prompt this customer to engage with your product.
Creating a persona provides a tangible reference point for your staff, ensuring all employees understand their typical customer’s wants and needs. The creation of personas enables precise messaging, better customer engagement, and increased conversion rates.
Product Messaging and Positioning
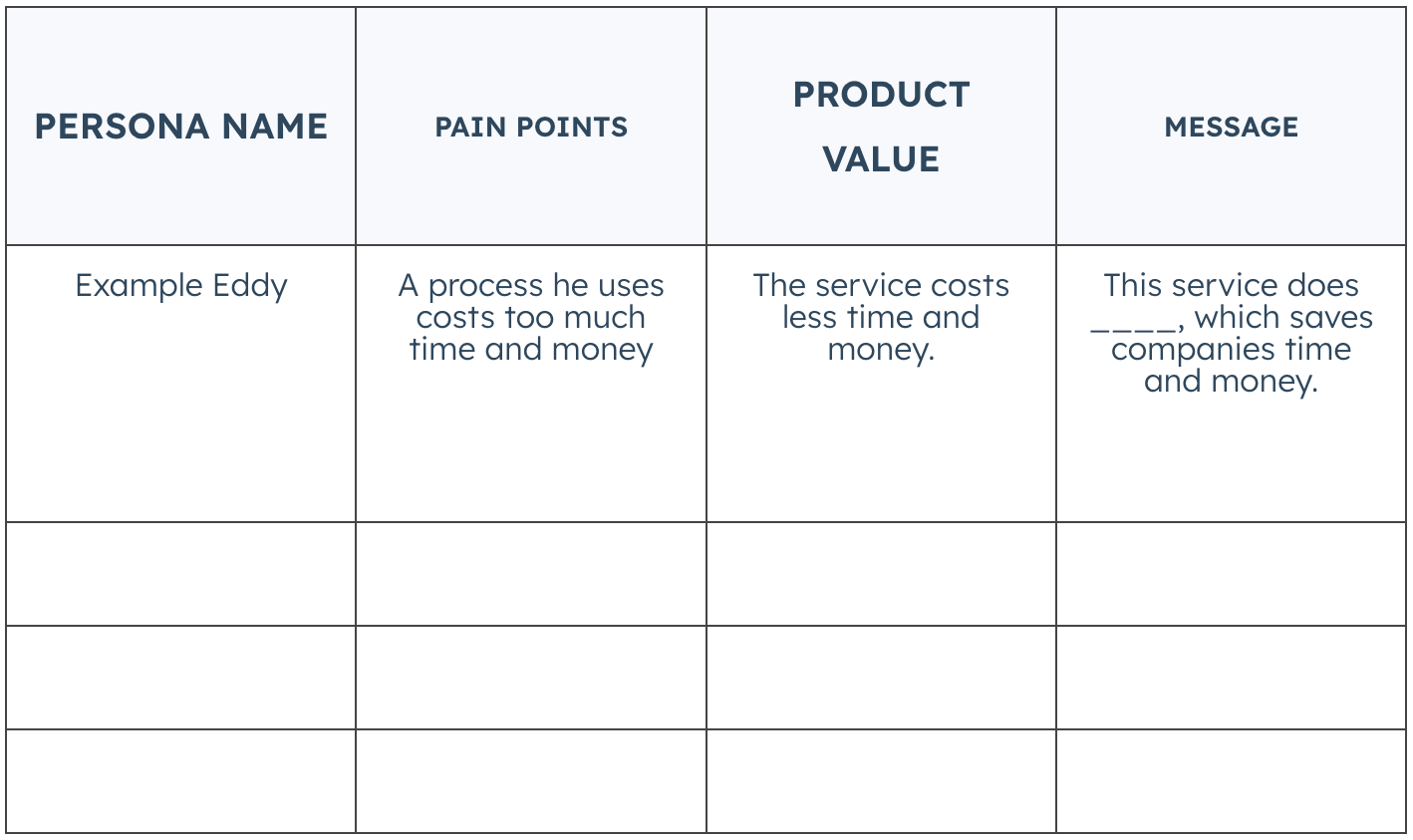
Product messaging and positioning is about forming a connection between your product offering and the target customer. Messaging revolves around the value proposition of your product to the customer, and should be coherent, clear, and convincing.
Positioning, on the other hand, involves defining where your product or brand stands in the market in comparison to your competitors. It helps guide marketing strategy by:
- Clarifying the brand’s essence
- Identifying the best positioning scenario
- Determining strategies necessary to win a position in the market you’ve targeted
Sales and Marketing Strategy
Your sales and marketing strategy signifies the path you’ll follow to reach your business goals. It broadly details your plan to persuade and convince potential customers to buy your product or service.
However, the best strategies contain actionable tactics that employ specific marketing concepts such as direct and indirect marketing, inbound and outbound marketing, and digital marketing.
Pricing and Revenue Model
Defining a pricing and revenue model remains a fundamental component of a successful go-to-market strategy. Your pricing strategy can significantly impact your brand’s positioning and competitiveness in the market.
Creating a robust revenue model ensures your business’s long-term sustainability and profitability. It is paramount to choosing the right pricing model for your product, consider using:
- Cost-plus model
- Competitive model
- Value-based model
- Freemium model
Each one has its pros and cons and should be carefully evaluated against your business goals and the market scenario.
Implementing Your GTM Strategy: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Unpack the stages of creating a compelling go-to-market strategy
- Learn ways to identify your target market, and stand out from competition
- Discover the power of a well-crafted sales plan, pricing strategy, and product launch.
Step 1: Market Research and Analysis
The first step in the journey of implementing your GTM strategy bearings with the rigorous process of market research and analysis. Becoming an expert in your target market isn’t an option but a necessity. It involves understanding your potential customers’ needs, pain points, and expectations.
Paying attention to key details can be used to your advantage, like:
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Behaviour patterns
These insights shape your subsequent approach and pave the way for a successful go-to-market process.
Step 2: Defining Your Unique Value Proposition
The second phase involves identifying your business’s USP (Unique Selling Proposition). This is a direct translation of what problem your product/service is solving and for whom. It’s about showcasing the distinctive edge your business holds over competitors.
By coupling the insights gathered from market research with careful consideration of your product benefits, you can craft a compelling value proposition that resonates with your target demographic.
Step 3: Developing Your Sales and Marketing Plan
A well-laid-out sales and marketing plan is paramount to the success of your go-to-market strategy. This step entails:
- Defining your marketing goals
- Crafting a compelling narrative for your brand
- Deciding on the channels to reach your target market
- Planning your sales process
It’s crucial to ensure that your marketing messages align with your value proposition and appeal to your target audience. Driving home the unique benefits of your product/service and showcasing its problem-solving capabilities is central to this stage.
Step 4: Launching Your Product or Service
The final step in your GTM implementation is arguably the most exciting-launching your product or service. This is the moment when all your hard work materializes. Your launch strategy should be driven by the insights gained from the previous steps, establishing a strong market presence from the start.
Interweaving elements of surprise, excitement, and unique buying propositions ensure a favorable response from your audience. It’s not just about launching, it’s about making a striking entrance to turn heads in the market.
Measuring the Success of Your GTM Strategy: 5 Key Metrics
- The reasons behind, and implications of, keeping a hawk-eye on your Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- How to extract the maximum value from your Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) statistics
- Effectively growing and maintaining your market share
- Speeding up your sales growth rate
- Techniques for increasing customer satisfaction and retention rate
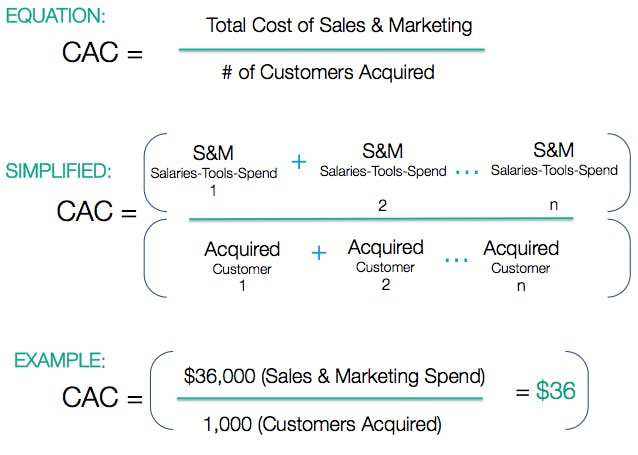
1. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
No startup can overlook the importance of accurately calculating their customer acquisition cost (CAC). This financial metric is all about understanding how much money you spend to gain each new customer. By identifying and reducing excess spending, startups can free up resources for other important areas.
Now, reducing your customer acquisition costs doesn’t necessarily involve cutting costs. Rather, it’s about the process of smartly allocating resources. Focus on driving your marketing and sales efforts towards the most responsive segments. Reduced wastage and more efficient spending are the tangible outcomes of a finely-tuned CAC.
2. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Another metric worth the attention is the customer lifetime value (CLV). The CLV metric is the total revenue you expect a single customer to generate over the lifespan of their business relationship with you. It’s a forecast of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer.
Increasing your CLV means generating more profit per customer. And doing so requires a top-down review of each customer interaction point, including:
- Marketing
- Sales
- Product usage
- Customer service
Intuitively, a higher CLV also leaves room for a higher CAC, presenting startups with increased financial flexibility.
3. Market Share
The market share metric is straightforward – it’s your company’s total sales over a specified period divided by the total sales of the industry over the same period. It can provide a quick snapshot of your startup’s standing in the marketplace.
Growing and maintaining your market share requires not only attracting new customers but also retaining existing ones.
Consider it as a cycle, where your marketing and sales efforts bring in new customers, and your product and customer success team work towards retaining these customers.
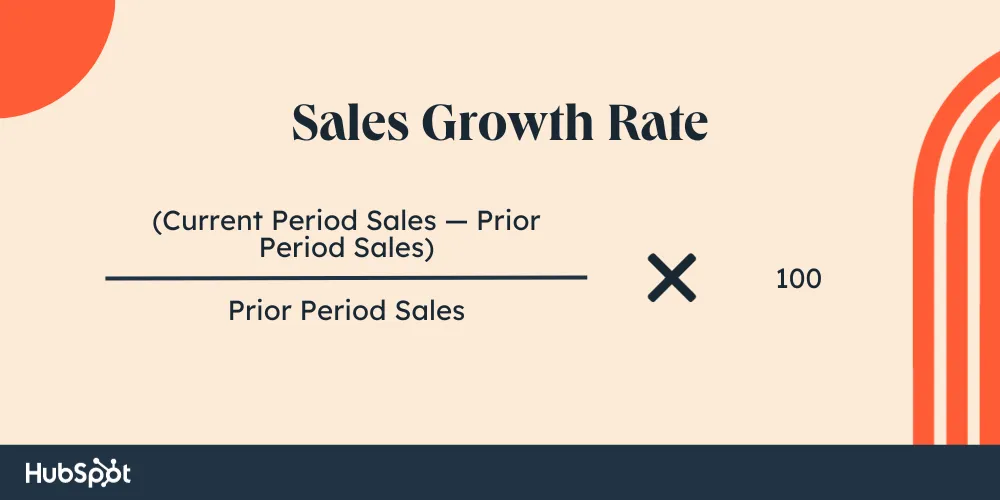
4. Sales Growth Rate
Tracking your sales growth rate is vital in measuring the effectiveness of your GTM strategy. It provides a benchmark against which you can evaluate the efficiency of your sales force.
Sales growth can be increased through a variety of channels, like:
- More effective advertising
- Innovative pricing strategies
- Enhanced product or service offerings
An increased sales growth rate is an indicator that your GTM strategy is resonating well with your target audience.
5. Customer Satisfaction and Retention Rate
Lastly, customer satisfaction and retention rate are clear indicators of your customers’ sentiment towards your product or services. The cost of acquiring a new customer can be five times more than retaining existing customers.
High customer retention and satisfaction rates signify a loyal customer base and are good predictors of referral rates.
Ensuring outstanding experience at each customer touchpoint must be a priority to achieve high customer satisfaction and retention rates.
The higher these metrics, the better your chances of organic growth.
3 GTM Strategies that Set B2B SaaS Startups Up for Success
B2B SaaS Startup Leaders – What go-to-market (GTM) strategies have you deployed to set your business up for success? Can you illustrate at least one example of this? Here is what 3 thought leaders have to say.
- Personalize Your GTM Strategy
- Build Strategic Industry Partnerships
- Focus on Vertical Market Segments
Personalize Your GTM Strategy
At Startup House, we have found that a personalized approach to our GTM strategy has been key to our success. By truly understanding the pain points and needs of our target B2B SaaS customers, we are able to tailor our messaging and solutions to meet their specific requirements.
One example of this is when we identified a common challenge among our clients in the healthcare industry and developed a specialized software solution that addressed their unique compliance and security needs. This not only helped us stand out in a crowded market but also built trust and loyalty with our customers.
Alex Stasiak, CEO & Founder, Startup House
Build Strategic Industry Partnerships
At Venture Smarter, we’ve taken a multi-faceted approach to ensure our business is set up for success. One of our key strategies revolves around building strategic partnerships with industry leaders. We’ve forged alliances with major players in various sectors relevant to our business, such as technology, infrastructure, and government.
For example, we recently partnered with a leading technology company to integrate their cutting-edge solutions into our platform. This collaboration not only enhances the functionality of our product but also gives us access to a broader customer base through our partner’s existing network. By leveraging these partnerships, we’re able to amplify our reach and credibility in the market.
Additionally, we’ve adopted a targeted marketing approach tailored to our audience segments. Instead of casting a wide net, we focus our efforts on specific industries and verticals where our solution can deliver the most value. This allows us to allocate resources more efficiently and engage with potential customers in a more meaningful way.
Jon Morgan, CEO, Venture Smarter
Focus on Vertical Market Segments
We’ve deployed several go-to-market strategies at TrackingMore to set up our business for success with a keen interest in vertical market focus. Our target B2B customers are in the logistics, supply chain, fulfillment, and e-commerce industries. Recently, we’ve narrowed down to these segments, focusing on how our tracking platform and tools can help them enhance shipment visibility and boost customer satisfaction. TrackingMore is also key in helping these businesses meet compliance requirements. We’ve tailored our marketing messages to highlight this and other unique features that our tracking solution offers. Interviewing existing B2B customers and sharing their success stories has also been a pillar of our go-to-market strategy.
Clooney Wang, CEO, TrackingMore
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Developing Your GTM Strategy
Avoidable mistakes in creating a GTM strategy are common among startups.
- Key missteps include overlooking market research, misinterpreting your target audience, and ineffective product positioning.
- Other pitfalls involve an unclear sales and marketing blueprint, along with improper pricing tactics.
- This section details each pitfall, allowing you to adopt proactive measures.
Neglecting Market Research
Foregoing extensive market research is akin to walking blindfolded on an unknown path. Without understanding the market landscape, startups risk launching products or services in saturated or non-existent markets.
You need to know your competitors, market trends, and the overall economic climate before creating your GTM strategy. Otherwise, you risk wasting resources and missing crucial opportunities.
Misunderstanding Your Target Audience
Failing to recognize your target audience accurately is another common pitfall. You must know whom your product or service caters to by comprehending and hypothesizing their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
By not knowing your target audience, you risk launching a product unfit for its intended consumers, leading to poor reception and potentially negative feedback. As we mentioned earlier, creating a customer persona can help ensure you’ve considered every aspect of your ideal buyer, meaning you can customize and personalize the journey.
Ineffective Product Positioning
Product positioning that doesn’t hit the mark can lead to your product being overlooked or misunderstood.
Effective product positioning communicates the benefits and value proposition of your product to your target audience clearly, ensuring it stands out in a crowded market.
A lack of effective product positioning may revolve around:
- An unclear value proposition
- Improper messaging
- Lack of understanding of the market and competition
Lack of Clear Sales and Marketing Strategy
In the haste of launching a product, many startups neglect a comprehensive sales and marketing strategy. An unclear plan may result in:
- Disjointed efforts
- Poor customer reach
- Lackluster sales
- Inefficient use of resources
A clear strategy should include a well-defined sales process, a marketing plan that aligns with your target audience, and benchmarks to measure success. Remember to make a cohesive content marketing strategy that uses multiple channels where the majority of your audience hangs out.

Inadequate Pricing Strategy
Pricing is more than just covering costs and profits. An inadequate pricing strategy can lower perceived product value and discourage potential customers.
Pricing should reflect the product’s value to customers, its positioning in the market, and factors like production costs and customer affordability. A competitive pricing model can tip the scales in your favor in a competitive market. Neglecting this aspect can negatively impact your market entry and profitability.
Winning the GTM Strategy Game
Setting accurate target markets, balancing internal and external factors, and defining success measures are foundational to constructing formidable go-to-market strategies. Embedding flexibility and iterative learning in the process will be pivotal in driving your startup’s growth trajectory.
How critical has identifying the right target audience been to your own GTM plan? Keep this question in mind as you leverage this framework and weave your distinctive GTM blueprint.
Next, it’s time to put these insights into practice. Envision your promising startup navigating the competitive business terrain with a winning GTM strategy-one that is unique, flexible, and reflective of your startup’s core values.
Remember, the strength of your GTM strategy lies in its simplicity and its focus on the unique value your startup brings. Now, it’s your turn to make a mark.

