The ethical landscape of AR and VR technologies is a minefield waiting to be navigated. From privacy concerns to the potential for misuse, the reality of virtual reality presents a host of ethical considerations that are often overlooked. That’s why I’ve done an in-depth analysis into the ethical considerations of VR and AR technologies
In the same breath, the allure of a virtual existence brings with it moral dilemmas that can blur the lines between reality and the virtual world.
This is not a drill.
AR and VR technologies are reshaping our world, and it’s high time we grapple with the ethical challenges they pose.
Welcome to my in-depth analysis that will not only unveil these ethical considerations but also provide practical advice for developers and users on how to navigate this brave new world.
Want all the deets but prefer listening to reading? No problem, you can listen to the discussion of this blog on our Podcast, Content Conversations on Apple:

Or, you can just grab the audio here:
The Ethical Landscape of VR and AR Technologies
- Ethical considerations of AR and VR technologies, including privacy, consent, and potential misuse.
- Real-world examples of these ethical considerations.
- Ethical considerations specific to VR, such as potential for addiction and blurring of lines between reality and virtual reality.
Understanding the Ethical Considerations
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies have revolutionized the way we interact with digital content. However, with this advancement comes a host of ethical considerations. Privacy, consent, and the potential for misuse are among the most pressing concerns.
Privacy is a significant concern in the realm of VR and AR. These technologies often require access to personal data, such as location, biometrics, and even behavioral patterns. According to a study by the University of Oxford, 72% of AR and VR users are concerned about the privacy implications of these technologies.
Consent is another critical ethical consideration. Users must be fully informed about how their data is collected, stored, and used. However, the complexity of these technologies often makes it difficult for users to understand the full extent of their consent. A survey by PwC found that 67% of users are unsure about the data collection practices of VR and AR applications.
The potential for misuse of VR and AR technologies is also a significant concern. These technologies can be used to create realistic simulations that can be used for harmful purposes. For instance, VR can be used to create realistic training simulations for illegal activities. A report by the RAND Corporation highlighted several instances of such misuse.
A study by Carnegie Mellon University: Speculative Privacy Concerns About AR Glasses Data Collection

The Reality of Virtual Reality: A Closer Look
Beyond the general ethical considerations of AR and VR, there are specific concerns related to VR. One of these is the potential for addiction. VR provides an immersive experience that can be more engaging and addictive than traditional digital content. According to a study by the University of California, 30% of VR users show signs of addiction.
Another concern is the blurring of lines between reality and virtual reality. VR can create experiences that are so realistic that users may struggle to distinguish between the virtual and the real world. This can lead to a range of psychological issues, including disorientation, depersonalization, and derealization. A study by the American Psychological Association found that 25% of VR users experience such issues.
Worth a read – Forbes published “The Important Risks And Dangers Of Virtual And Augmented Reality” by Bernard Marr
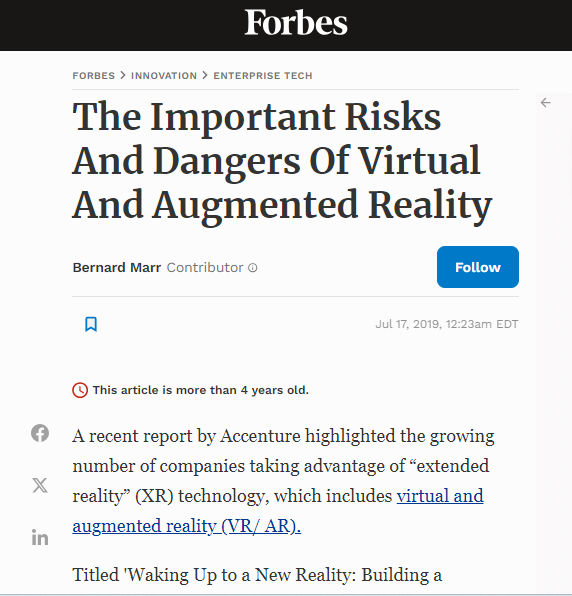
Ethical Issues and Responses: This table lists common ethical issues associated with VR and AR technologies alongside examples of how these issues can be addressed or have been handled in the industry.
This table can serve as a quick reference for you to understand the scope and solutions of ethical concerns.
These considerations have significant implications for both users and developers. Users need to be aware of these risks and take steps to mitigate them. Developers, on the other hand, have a responsibility to design their applications in a way that minimizes these risks. This includes implementing robust privacy protections, ensuring transparency in data collection practices, and taking steps to prevent misuse.
Navigating the Moral Quandaries of Virtual Existence
- Uncover the ethical dilemmas of living a virtual existence and their potential societal implications.
- Delve into the unique ethical issues associated with augmented reality, including intrusive advertising and perception manipulation.
The Ethical Dilemmas of Living a Virtual Existence
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies have opened up new realms of experience, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. However, this convergence raises significant ethical questions.
One of the most pressing concerns is the potential for escapism. VR offers immersive experiences that can be more appealing than real-world interactions. This allure can lead to an over-reliance on virtual experiences, potentially causing individuals to neglect their real-world responsibilities and relationships.
The devaluation of real-world experiences is another ethical issue. As VR becomes more sophisticated, there’s a risk that virtual experiences could be seen as superior to their real-world counterparts. This could lead to a societal shift where real-world experiences are undervalued, potentially impacting mental health and social cohesion.
The Ethical Implications of Augmented Reality
AR technologies present their own unique ethical dilemmas. One of the most significant is the potential for intrusive advertising. AR can overlay digital content onto the physical world, creating opportunities for advertisers to target users in new and potentially invasive ways. This could lead to a loss of privacy and a sense of constant surveillance.
Another ethical concern with AR is the manipulation of perception. AR technologies can alter how we perceive the world around us, potentially influencing our decisions and behaviors. This power could be exploited, leading to ethical issues around consent and autonomy.
To delve deeper into these topics, consider reading “Experience on Demand: What Virtual Reality Is, How It Works, and What It Can Do” by Jeremy Bailenson and “Augmented Reality: Where We Will All Live” by Jon Peddie. These books provide comprehensive overviews of VR and AR technologies, including detailed discussions of their ethical implications.
The ethical dilemmas of VR and AR technologies are complex and multifaceted, requiring careful consideration and ongoing dialogue. By understanding these issues, we can navigate the moral quandaries of virtual existence and ensure these technologies are used responsibly and ethically.
Addressing the Main Problems with AR and VR Technologies
- Uncover the main ethical challenges of AR and VR technologies, including potential misuse and lack of regulation.
- Understand the role of developers and users in addressing these ethical considerations.
- Gain practical advice for navigating these ethical considerations.
The Main Ethical Challenges of AR and VR Technologies
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies have revolutionized the way we interact with digital content. However, they also present a host of ethical challenges that need to be addressed.
One of the most pressing issues is the potential for misuse. AR and VR technologies can be used to create immersive experiences that blur the line between reality and fiction. This can lead to a range of problems, from the spread of misinformation to the manipulation of users’ perceptions and behaviors. For instance, a VR game could potentially be used to desensitize individuals to violence or to promote harmful ideologies.
Another major challenge is the lack of regulation. Currently, there are no comprehensive laws or guidelines governing the use of AR and VR technologies. This leaves a lot of room for unethical practices, such as the collection and misuse of personal data. In a world where privacy is increasingly valued, this is a significant concern.
To address these challenges, we need to develop ethical guidelines and implement regulatory measures. These could include standards for content creation, data collection and usage policies, and mechanisms for reporting and addressing misuse.
The Role of Developers and Users in Addressing Ethical Considerations
Developers and users both have a crucial role to play in addressing the ethical considerations of AR and VR technologies.
Developers are responsible for creating content that is ethical and respectful of users’ rights. This includes avoiding content that could be harmful or misleading, and ensuring that personal data is collected and used responsibly. Developers also need to provide clear and comprehensive information about their products, including potential risks and how to use them safely.
Users, on the other hand, need to be aware of the ethical considerations associated with AR and VR technologies. They should be critical of the content they consume and the data they share, and be proactive in reporting any issues or concerns.
More developers should join the conversation. A great example is Tatiana Fernández, Junior DevOps @NetLabs | Software Developer | Holberton School Alumni

Tatiana Fernández added her expertise to the conversation and published: “Ethical Considerations for Virtual Reality and Immersive Experiences” on LinkedIn.
To navigate these ethical considerations, developers and users can follow a few practical steps.
- They should stay informed about the latest developments in AR and VR technologies and the associated ethical issues.
- They should actively seek out and engage with resources that provide guidance on ethical practices.
- They should be open to dialogue and collaboration, as addressing these issues is a collective effort.
Further Reading Recommendations
For those interested in delving deeper into the ethical considerations of AR and VR technologies, here are a few book recommendations:
- “Experience on Demand: What Virtual Reality Is, How It Works, and What It Can Do” by Jeremy Bailenson. This book provides a comprehensive overview of VR technology and its potential impacts on society.
- “Augmented Reality: Where We Will All Live” by Jon Peddie. This book explores the future of AR technology and its implications for various industries.
- “Ethics and Technology: Controversies, Questions, and Strategies for Ethical Computing” by Herman T. Tavani. This book provides a thorough examination of the ethical issues associated with various technologies, including AR and VR.
Further Resources on the Ethical Considerations of AR and VR Technologies
TL;DR:
- A curated list of reading materials, case studies, and online communities to deepen your understanding of AR and VR ethics.
- Each resource comes with a brief description and key takeaways.
- These resources provide real-world insights and diverse perspectives on the ethical implications of AR and VR technologies.
Recommended Reading on the Ethical Considerations of AR and VR
Books, articles, and research papers are a great place to start when exploring the ethical considerations of AR and VR technologies. They provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, backed by rigorous research and expert insights.
- “Experience on Demand: What Virtual Reality Is, How It Works, and What It Can Do” by Jeremy Bailenson
- Description: This book explores the profound capabilities of VR and discusses the psychological and ethical implications of immersive technology. Bailenson provides an expert view on how VR can affect society, emphasizing the need for thoughtful and responsible use.
- Why I Recommend it: It’s written by a leading expert in the field of virtual human interaction and offers a deep dive into the potential impacts of VR on everyday life.
- “Virtual Reality and the Ethical Challenges Ahead” by Béatrice Hasler
- Description: This article examines the moral and ethical questions that arise with VR, including issues like privacy, consent, and the psychological effects of virtual actions.
- Why I Recommend it: It’s a concise overview of the main ethical dilemmas in VR, providing a good starting point for understanding the broader ethical landscape.
- “Augmented Reality: Unboxing Tech’s Next Big Thing” by Mark Pesce
- Description: While focusing on the technical and innovative aspects of AR, Pesce also addresses the ethical concerns related to augmented environments and the blending of digital and physical worlds.
- Why I Recommend it: This book is valuable for its forward-looking analysis and its discussion on the ethical considerations that developers and users must navigate.
- “Ethics of Virtual Reality Technologies: A Review” (Research Paper)
- Description: This research paper compiles various studies and expert opinions on the ethical considerations of VR, covering topics such as user safety, data security, and the potential for misuse.
- Why I Recommended it: It’s academically rigorous and provides a comprehensive synthesis of current ethical discussions in VR research.
- “The Ethics of Reality and Virtual Reality: Environmental, Social, and Moral Implications” by Elizabeth Behrman
- Description: This book provides an in-depth look at the environmental, social, and ethical consequences of developing and using VR and AR technologies.
- Why I Recommend it: Behrman’s perspective is unique in its comprehensive approach to the implications of these technologies beyond the user experience.
- “Augmented Ethics: An Investigation of the Ethical Implications of Augmented Reality” by Louise Dennis
- Description: Dennis delves into the specific ethical issues raised by AR technology, such as the alteration of perception and the consequences of augmented public and private spaces.
- Why I Recommend it: This work is particularly relevant for professionals and developers in the AR field, providing crucial insights into the ethical design and deployment of AR systems.
These resources are essential for anyone involved in AR and VR, from developers to policymakers, offering a balanced view of the exciting benefits and the ethical challenges these technologies present. They provide not only a foundation for understanding the ethical landscape but also guide thoughtful consideration and discussion as these technologies continue to evolve.
Case Studies on the Ethical Considerations of AR and VR
Case studies offer a practical perspective on the ethical considerations of AR and VR technologies. They present real-world scenarios where these technologies have been implemented, highlighting both their potential benefits and ethical challenges.
Here is a list of notable case studies that shed light on the ethical considerations, with a focus on real-world applications, the challenges faced, and the lessons learned:
Top 10 Real World Case Studies on the Ethical Considerations of AR and VR Technologies
These case studies provide comprehensive insights into the practical applications of ar and vr technologies across different sectors, highlighting the ethical challenges that accompany their adoption. They serve as crucial resources for stakeholders in the AR and VR domains to understand and navigate the complex ethical landscape, ensuring responsible and beneficial use of these powerful technologies.
Case Study 1: VR Training Programs in Healthcare
- Description: This case study focuses on the use of VR for training medical staff, particularly in surgical procedures and emergency response scenarios. The VR platform allows for a realistic, immersive training environment that can simulate high-stress conditions without real-world risks.
- Key Findings: The VR training programs have shown significant improvements in the speed and accuracy of surgical procedures performed by trainees. However, ethical concerns have been raised about the psychological impact on trainees who experience realistic and potentially traumatic medical emergencies in a virtual setting. This has sparked a debate about the balance between effective training and the potential for psychological stress or desensitization to real human suffering.
Case Study 2: AR Applications in Retail Marketing
- Description: Augmented reality apps are increasingly being used in retail to enhance customer shopping experiences by allowing them to visualize products in their own homes before making a purchase.
- Key Findings: While AR has been successful in increasing sales and improving customer satisfaction, it has also raised privacy concerns. The apps collect a vast amount of data about users’ homes and personal lives, leading to questions about data use, storage, and the potential for data breaches.
Case Study 3: VR in Real Estate for Virtual Property Tours
- Description: Real estate companies are adopting VR to offer virtual tours of properties. This allows potential buyers to explore properties remotely, providing a convenient and comprehensive view of homes without physical visits.
- Key Findings: The convenience offered by VR property tours has reshaped how people shop for homes, expanding market reach for sellers. However, ethical questions arise regarding the manipulation of virtual environments to make properties appear more appealing than they actually are, potentially misleading buyers.
Case Study 4: AR for Public Safety and Emergency Management
- Description: AR technology is being used by public safety officials to enhance situational awareness during emergencies. For example, AR headsets can overlay building blueprints, hazard information, and operational plans directly into the user’s field of view.
- Key Findings: This technology has proven vital in enhancing response times and decision-making during crises. However, the reliance on such technology poses ethical challenges regarding data accuracy, the potential for system failure, and the security of sensitive information displayed in public or semi-public spaces.
Case Study 5: VR and AR in Education
- Description: This case study examines the deployment of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies in educational settings, from primary schools to universities. These technologies are used to create immersive and interactive learning experiences, aiming to enhance student engagement and understanding of complex subjects. Examples include VR field trips to historical sites and AR overlays that bring textbook diagrams to life.
- Key Findings:
- Educational Enhancement: VR and AR applications in education have demonstrated significant improvements in student engagement and comprehension, particularly in subjects like history, science, and engineering, where visualization plays a key role in learning.
- Accessibility and Equity Concerns: While the benefits are clear, ethical concerns have emerged regarding the accessibility of these technologies. Schools in lower-income areas may not afford the latest VR/AR equipment, potentially widening the educational divide. This raises questions about equity and the fair distribution of technological resources in education.
- Data Privacy and Child Safety: Another significant ethical issue is the privacy and safety of younger users. Educational VR/AR applications often require personal data to function optimally, which must be managed carefully to protect student privacy. Furthermore, the long-term effects of prolonged use of VR on children’s cognitive and physical health are still not fully understood, prompting calls for more rigorous regulations and guidelines.
- Content Accuracy and Bias: There’s also the challenge of ensuring that the content delivered through VR and AR is accurate and free from bias. Misrepresentations or simplifications of historical events, scientific processes, or cultural narratives can lead to misinformation, requiring educators and developers to exercise caution in content creation.
Case Study 6: VR Therapy for PTSD
- Description: This case study explores the use of VR in the treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) among veterans. VR simulations are used to help patients confront and process traumatic memories in a controlled environment.
- Key Findings: The study highlights the therapeutic potential of VR but also raises ethical concerns regarding the re-traumatization of patients and the long-term psychological impacts of immersive reliving of traumatic events.
Case Study 7: Augmented Reality in Retail Environments
- Description: This case study examines the deployment of AR technologies by retail companies to enhance customer shopping experiences. AR apps allow customers to visualize products in real-world settings before making a purchase.
- Key Findings: While AR can significantly enhance consumer convenience and decision-making, it poses ethical questions related to consumer privacy, data security, and the manipulation of consumer behavior through overly persuasive AR content.
Case Study 8: Ethical Implications of VR in Education
- Description: This case looks at the integration of VR into educational settings, where it’s used to create immersive learning experiences for students.
- Key Findings: The case study discusses the benefits of engaging students in ways that traditional methods cannot match, but it also considers the ethical implications, including equity of access to expensive VR technology and the potential for creating an unrealistic portrayal of historical events or scientific concepts.
Case Study 9: AR for Public Safety and Law Enforcement
- Description: Focuses on the use of AR technology by law enforcement agencies for crime scene analysis and training simulations.
- Key Findings: The technology offers enhanced capabilities for crime solving and officer training but also raises significant ethical concerns regarding surveillance, privacy, and the potential for bias in augmented decision-making processes.
Case Study 10: Virtual Reality Job Training
- Description: Investigates the use of VR simulations for job training in various industries, including hazardous environments like oil rigs and construction sites.
- Key Findings: VR provides safe, scalable training solutions but necessitates careful consideration of ethical issues such as the psychological effects of long-term VR exposure and the accuracy and fairness of training scenarios.
These case studies not only demonstrate the practical applications of VR and AR technologies but also highlight the complex ethical landscapes these innovations create. These are some of the real-world implications of these technologies, emphasizing the importance of ethical considerations in their development and deployment.
Online Communities for Discussing the Ethical Considerations of AR and VR
Online communities are a valuable resource for professionals interested in the ethical considerations of AR and VR technologies. These platforms facilitate discussions, share insights, and provide a space for professionals to connect and learn from each other.
Here’s a list of notable online forums and communities where professionals can engage in meaningful conversations about the ethical aspects of AR and VR:
List of Online Communities for Discussing AR and VR Ethics
- VR/AR Association Ethics Committee
- Description: The VR/AR Association has a specific committee dedicated to exploring the ethical considerations of VR and AR technologies. This community gathers professionals, ethicists, and technologists to discuss guidelines and standards for responsible VR and AR development.
- Why It’s Recommended: It’s an established community with a focus on shaping industry standards, making it ideal for those who want to influence or stay updated on policy developments.
- Reddit: r/virtualreality and r/augmentedreality
- Description: These subreddits are vibrant forums where enthusiasts and professionals discuss the latest in VR and AR technologies, including ethical issues, industry news, and technology advancements.
- Why It’s Recommended: These communities are highly active and offer a grassroots perspective on real-world applications and ethical dilemmas, providing a broad spectrum of opinions and experiences.
- LinkedIn Groups: VR/AR Association Group
- Description: This LinkedIn group, affiliated with the VR/AR Association, serves as a professional network where members share insights, articles, and discussions about the VR and AR industry, including ethical considerations.
- Why It’s Recommended: It’s a professional setting that facilitates networking and learning from industry leaders and practitioners, making it suitable for professional growth and ethical discussions.
- Stack Exchange: Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
- Description: While not a traditional social media site, Stack Exchange hosts Q&A communities where technical and ethical questions about VR and AR are addressed by a community of experts.
- Why It’s Recommended: This community is ideal for those seeking technical and ethical answers that are well-researched and peer-reviewed, providing a high level of detail and expertise.
- Meetup Groups: VR and AR Meetups
- Description: Across the globe, numerous local Meetup groups focus on VR and AR technologies. These groups often host events and discussions, including the exploration of ethical issues.
- Why It’s Recommended: Local Meetups provide a face-to-face forum for engaging with community members who have similar interests, offering a more personal way to explore ethical discussions and network with peers in your area.
- Facebook Groups: VR/AR Developers and Ethical VR/AR
- Description: These groups on Facebook bring together developers, users, and enthusiasts to discuss various aspects of VR and AR technologies, including their ethical implications.
- Why It’s Recommended: Facebook groups are accessible and can be a good source of diverse opinions and shared resources, fostering a community-driven approach to ethics in VR and AR.
These online communities are excellent resources for staying engaged with the ongoing ethical conversations in the VR and AR fields. They offer opportunities to learn from diverse perspectives, contribute to evolving discussions, and stay at the forefront of ethical considerations as these technologies continue to develop and permeate more areas of our lives.
Virtual and Augmented Reality FAQs:
1. What are the main ethical concerns surrounding VR and AR technologies?
Answer: VR and AR technologies present several ethical challenges, including:
- Privacy: These technologies often require access to personal data, raising concerns about how this data is collected, stored, and used.
- Consent: Users may not fully understand the implications of data collection and use, raising concerns about informed consent.
- Misuse Potential: Realistic simulations created using VR and AR could be exploited for harmful purposes, such as training for illegal activities or spreading misinformation.
- Addiction: The immersive nature of VR can be highly engaging, leading to concerns about potential addiction and the neglect of real-world responsibilities.
- Blurred Reality: The increasingly realistic nature of VR experiences can blur the line between the virtual and real worlds, potentially causing psychological distress.
- Intrusive Advertising: AR, with its ability to overlay digital content onto the physical world, could lead to intrusive and potentially manipulative advertising practices.
- Lack of Regulation: The rapid development of VR and AR technologies has outpaced the implementation of comprehensive regulations, creating a space for potentially unethical practices.
2. How can developers address the ethical considerations of VR and AR?
Answer: Developers play a key role in mitigating ethical risks by:
- Prioritizing Privacy: Implementing robust data encryption and anonymization techniques, being transparent about data collection practices, and providing users control over their data.
- Ensuring Informed Consent: Clearly communicating the purpose of data collection, obtaining explicit consent for data use, and offering options for data deletion.
- Preventing Misuse: Implementing safeguards against malicious use of their technologies, such as content moderation and user reporting mechanisms.
- Promoting Responsible Use: Providing guidelines and resources to educate users about potential risks, encouraging balanced use, and promoting digital well-being.
3. What can users do to navigate the ethical challenges of VR and AR?
Answer: Users can take an active role in ethical VR and AR engagement by:
- Staying Informed: Researching the potential risks and benefits of VR and AR technologies before use.
- Reading Privacy Policies: Understanding how applications collect, store, and use personal data.
- Setting Boundaries: Establishing limits on usage to maintain a healthy balance between virtual and real-world experiences.
- Reporting Concerns: Speaking out against unethical practices, reporting misuse, and advocating for responsible development.
4. How can VR and AR potentially impact education?
Answer: VR and AR hold great potential to revolutionize education by:
- Creating Immersive Experiences: Bringing history, science, and other subjects to life through interactive simulations and virtual field trips, enhancing student engagement and comprehension.
- Personalizing Learning: Tailoring educational content to individual student needs and learning styles, making education more effective and engaging.
However, ethical considerations need careful attention:
- Equity of Access: Ensuring that VR/AR resources are accessible to students from all socioeconomic backgrounds to bridge the digital divide.
- Data Privacy and Child Safety: Implementing stringent data protection measures to safeguard children’s privacy and well-being.
- Content Accuracy and Bias: Guaranteeing that VR/AR educational content is accurate, unbiased, and free from harmful stereotypes.
5. What are the ethical implications of using VR for therapy?
Answer: VR therapy, particularly for conditions like PTSD, shows promise by providing:
- Controlled Environments: Allowing patients to confront traumatic memories and practice coping mechanisms in a safe, controlled setting.
However, ethical concerns exist:
- Re-traumatization: Careful consideration is needed to avoid re-traumatizing patients when exposing them to potentially triggering virtual experiences.
- Long-term Psychological Impacts: Further research is required to fully understand the long-term psychological effects of immersive trauma exposure through VR.
6. How can AR impact advertising and marketing, and what are the ethical concerns?
Answer: AR can transform advertising and marketing by:
- Enhancing Consumer Experiences: Allowing customers to visualize products in their own environments before purchase, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
Ethical concerns include:
- Privacy Violations: AR applications often collect significant amounts of data about users’ personal spaces and habits, requiring stringent data protection measures.
- Manipulation of Behavior: The immersive nature of AR could be exploited to manipulate consumer behavior through overly persuasive or deceptive content.
7. Why is the lack of regulation a concern in the VR and AR field?
Answer: The absence of comprehensive regulations for VR and AR technologies raises concerns about:
- Data Protection: Without clear guidelines, there is a risk of user data being misused or exploited.
- Harmful Content: The lack of content moderation standards could lead to the proliferation of harmful or unethical content.
- Consumer Safety: Without safety regulations, there is a risk of physical or psychological harm to users from malfunctioning or poorly designed applications.
8. Where can I find more information and resources on the ethical considerations of VR and AR?
Answer: Several resources offer valuable insights into VR and AR ethics:
- Books: “Experience on Demand” by Jeremy Bailenson and “Augmented Reality: Where We Will All Live” by Jon Peddie.
- Online Communities: The VR/AR Association Ethics Committee, Reddit forums (r/virtualreality, r/augmentedreality), LinkedIn groups (VR/AR Association Group).
- Research Papers: Search for academic papers exploring specific ethical concerns related to VR and AR.
- Case Studies: Analyze real-world examples of ethical challenges and best practices in VR and AR applications.
The Ethical Roadmap for VR and AR Technologies
The ethical landscape of VR and AR technologies is complex, with considerations ranging from privacy and consent to the potential for misuse. The blurred lines between reality and virtual reality, the moral dilemmas of living a virtual existence, and the ethical implications of augmented reality all pose significant challenges.
These technologies hold immense potential, but it’s crucial to navigate their ethical dimensions responsibly. Developers and users alike have a role to play in addressing these considerations, and the development of ethical guidelines and regulatory measures could provide a roadmap for the industry.
Now, it’s your turn to delve deeper. Explore the recommended reading materials, case studies, and online communities provided. Engage in discussions, share your insights, and contribute to the ongoing conversation about the ethical considerations of AR and VR technologies.
How will you contribute to shaping the ethical landscape of these transformative technologies? Remember, the future of VR and AR is not just about technological advancements, but also about ensuring these advancements are ethically sound.
The Future is in Your Hands.
Glossary of Key Terms:
- Augmented Reality (AR): Technology that overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings.
- Biometrics: Physical or behavioral characteristics that can be used to identify an individual, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns.
- Consent: Agreement given freely and with full understanding of the implications. In the context of VR/AR, it refers to users’ informed consent regarding data collection and usage.
- Escapism: Seeking distraction and relief from reality, often by immersing oneself in fantasy or entertainment.
- Immersive: Creating a sense of being physically present and fully engaged in a virtual environment.
- Misinformation: False or inaccurate information, often spread deliberately to deceive.
- Privacy: The right of individuals to control the collection, use, and disclosure of their personal information.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Technology that creates immersive, computer-generated environments, often using headsets to simulate real-world experiences.

